City transport system needs a specialized approach to suit conditions of roads in different cities in India. City roads are generally narrow, congested and invariably encroached on both sides. Hill roads are also equally narrow. The operation of wide-body buses poses several problems. Moreover, the speed can rarely exceed 40/50 kph. Besides, fuel consumption increases more than 50 per cent of the designed mileage.

Buses for Indian roads should be designed with width not exceeding 2.2 meters. However, wide-body buses of 2.5/2.6 meter wide can be operated on the central dedicated lanes of Delhi Ring Road.
Electric buses which are indigenously designed, developed and built can substantially improve the economy of the whole system and increase the overall life. Except the chassis of trams, all types and sizes are indigenously available.
The following are several possible cost-effective short gestation options suggested for assembly of new buses based on the electric propulsion system:
It may be mentioned that most of the equipment for electric propulsion system and expertise for EVs, buses, etc., are available in India. Considerable work has been undertaken at IIT, Delhi. The basic technology was successfully designed, developed and put into operation within the campus. The chassis were supplied by Eicher and Tata Motors. There are about 150,000 buses operating in India. It is economically feasible to convert standard diesel buses to battery/electric system (AC or non-AC).
The tram technology is very old and was in operation in Delhi and Mumbai years ago. It is still in operation in Kolkata. However, modern tram systems have been developed and fabricated indigenously with some support from overseas companies. They are suitable for intra-city operation, on surface or elevated track. This technology is much superior to and economical as compared to the mono-rail system.
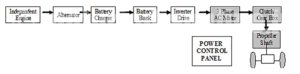
The electric propulsion system is the heart of any electric vehicle. It is based upon an electric drive consisting mainly of a motor and its controller. The source of power is hybrid of a battery bank + a low power genset using diesel, bio-diesel or LPG/CNG.
By H.K. Agarwal, Chartered Engineer (C. Eng. IETE), Sympar Associates