India’s automobile industry is set to change significantly with the enforcement of the BS-VI emission norms and proliferation of electric vehicles (EVs). While the BS-VI emission norms will have a more near-term impact, the effect of EVs will be felt in the medium to long-term.
The auto-casting industry in India, with revenue of ~Rs. 50,000 crores in fiscal 2018, can be categorised into ferrous and non-ferrous segments. The industry comprises major engine components such as cylinder heads, cylinder blocks, gear housing, and braking components such as brake drums and housings, clutch and flywheel housing.
So how will the transition from the BS-IV to the VI emission norms and adoption of electric vehicle impact the auto-casting industry?
On April 1, 2020, India will transition from the BS-IV straight to the BS-VI emission norms, skipping the BS-V stage. These norms are expected to impact the whole automobile industry, barring the tractor segment, which has, therefore, not been included in this analysis.
CRISIL expects the BS-VI emission norms to affect the auto-casting industry only slightly. While two-wheelers will feel the brunt, the net value of auto-castings within this segment is expected to remain largely unchanged.
In the case of cars and utility vehicles, CRISIL does not envisage a significant change because of the low share of diesel vehicles. In commercial vehicles, changes are expected in engine components and the exhaust management system, which have a low impact on auto-casting.
Nevertheless, BS-VI norms will lead to addition of both non-cast components and more electricals / sensors and changes in electronic control unit (ECU), which will push up prices across vehicle segments. Therefore, advancement in sales, particularly in the commercial vehicle segment, is anticipated.
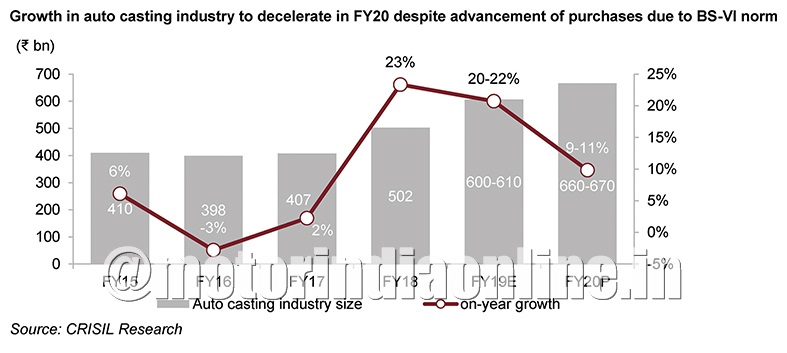
As per CRISIL estimates, auto-castings sales (in value terms) are expected to grow 9-11% in fiscal 2020, largely driven by volume growth owing to expected advancement of sales in fiscal 2020, ahead of the institution of BS-VI norms.
What risks do EVs pose for the auto-casting industry? With environmental pollution concerns mounting across the world, the push for vehicles running on alternative fuel sources has gained momentum. With battery costs plunging in the last few years, EVs are fast emerging as a desirable option.
Proliferation of EVs poses a threat to the traditional internal combustion engines (ICE). Major casted engine components such as cylinder heads, cylinder blocks, and gear housing (comprising around 50% of casted components) run the risk of becoming obsolete. ICE is expected to be replaced by lithium ion and other such batteries.
Keeping in mind the imminent threats, auto-casting players are adopting the following approaches to offset reduction in ICE component demand:
- Working with global and domestic original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) to develop motor housing, battery housing, knuckles, and turbochargers, to be used in electric vehicles.
- Making strategic investments in foreign companies which have existing electric powertrain solutions with potential to be leveraged in India.
- Setting up plants and expanding capacities to develop lightweight components for two-wheelers, and passenger, hybrid and electric vehicles.
Source: CRISIL Research