Exports fare even better with 24% jump
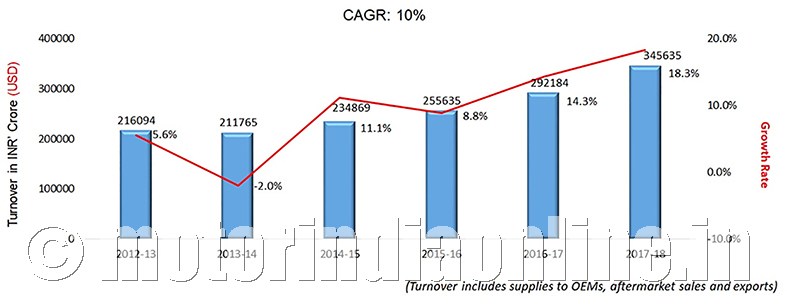
The turnover of the Indian automotive component industry that contributes 2.3 per cent to India’s GDP and has a share of 4 per cent in India’s exports stood at Rs. 3.45 lakh crores ($51.2 billion) for the period April 2017 to March 2018, registering a growth of 18.3 per cent over the previous year.

This is as per the figures released by the Automotive Component Manufacturers Association of India (ACMA) in its Industry Performance Review for fiscal 2017-2018.
The above data represents the supply from the auto component industry (ACMA members and non-members), on-road and off-road vehicle manufacturers and the aftermarket in India along with exports. The data also includes component supplies captive to the OEMs.
Commenting on the performance of the auto component industry in India, Mr. Vinnie Mehta, Director General, ACMA, said: “The year gone by witnessed an upswing in the overall performance of the vehicle industry, despite it facing several regulatory challenges. The component industry, in tandem, posted an encouraging performance with significant growth of 18.3 per cent over the previous fiscal, registering a turnover of Rs. 3,45,635 crores ($51.2 billion). Further exports grew by 23.9 per cent in FY 2017-18 to Rs. 90,571 crores ($13.5 billion)”.

Speaking about the need for Government intervention to sustain long-term growth in the auto component industry, Mr. Nirmal Minda, ACMA President, said: “The dynamics of the automotive market is undergoing a significant transformation as the industry strives to become compliant to various regulations related to emissions, safety and environment, including the transition from BS-IV to BS-VI. That apart, key trends such as vehicle connectivity, electrification of vehicles, shared mobility and Industry 4.0, among others, are also redefining mobility. To support the changing customer needs and to stay relevant, the auto component sector needs to be encouraged with supportive Government policies.”
He added: “One of the key demands of the industry has been a uniform 18% GST rate across the auto component sector; currently 60 per cent of the auto components attract 18 per cent GST rate, while the rest 40 per cent, majority of which are two-wheelers and tractor components, attract 28 per cent. The latter high rate has led to flourishing grey operations in the aftermarket. A benign rate of 18 per cent will not only ensure better compliance, but will also ensure a larger tax base. Further, considering the significant technological changes that the industry is undergoing, there is a critical need for creating a fund to support indigenous R&D and technology creation in the component industry as also for technology acquisition from other parts of the world. Lastly, as we prepare for the introduction of electric mobility in the country, a well defined, technology agnostic road-map with clear responsibilities of each stakeholder will go a long way in ensuring a smooth roll out as also leading to creation of a local supply base for the same”.
Key findings of the ACMA review
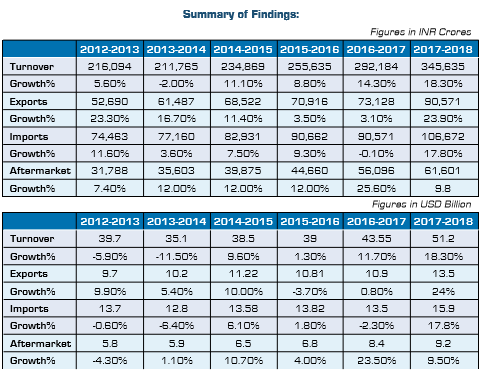
Exports of auto components grew by 23.9 per cent to Rs. 90,571 crores ($13.5 billion) from Rs. 73,128 crores ($10.9 billion) in 2016-17. Europe accounted for 34 per cent of exports, followed by North America and Asia, with 28 per cent and 25 per cent respectively.
The key export items included drive transmission & steering, engine components, body/chasis, suspension & braking, etc.
Imports of auto components increased by 17.8 per cent to Rs. 1,06,672 crores ($15.9 billion) in 2017-2018 from Rs. 90,571 crores ($13.5 billion) in 2016-2017. Asia accounted for 60 per cent of imports followed by Europe and North America, with 30 per cent and 8 per cent respectively.
With the expanding vehicle base in the country, the aftermarket in 2017-18 grew by 9.8 per cent to Rs. 61,601 crores ($9.2 billion) from Rs. 56,096 crores ($8.4 billion) in the previous fiscal.
Turnover data represents the entire supplies from the auto component industry (ACMA members and non-members) to the on-road and off-road vehicle manufacturers and the aftermarket in India as well as exports. This also includes component supplies captive to the OEMs and by the unorganized and smaller players.