At the end of 2013, the European Parliament and the Council of the European Union reached an agreement regarding two regulatory proposals that will implement mandatory 2020 CO2 emission targets for new passenger cars and light commercial vehicles in the European Union. The passenger car standards are 95 g/km of CO2, phasing in for 95 per cent of vehicles in 2020 with 100 per cent compliance in 2021. The light commercial vehicle standards are 147 g/km of CO2 for 2020.
The EU first introduced mandatory CO2 standards for new passenger cars in 2009. This regulation set a 2015 target of 130 g/km for the fleet average of all manufacturers combined. Individual manufacturers were allowed a higher CO2 emission value, depending on the average vehicle weight of their fleet. The heavier the average weight of the cars sold by a manufacturer, the higher the CO2 level allowed. A similar CO2 standard for new light commercial vehicles was introduced in 2011. It set a target of 175 g/km for 2017.
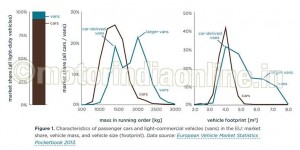
Light commercial vehicles make up about 10 per cent of light-duty vehicles in the EU, and they are often referred to as ‘vans’. Generally, there are two different types of light commercial vehicles:
1. Car-derived vehicles (e.g., VW Caddy), on average having a footprint (wheelbase × track width) of about 4 m2 and a mass of about 1,500 kg. As illustrated in Figure 1, they are very similar to typical passenger cars, such as the VW Golf.
2. Larger vans (e.g., Mercedes-Benz Sprinter), being more truck-like, typically with a footprint of more than 6 m2 and a vehicle mass of 2,000 kg or more (Figure 1).
The maximum gross vehicle weight of a light commercial vehicle is 3,500 kg.
In July 2012, the European Commission put forward two regulatory proposals to set mandatory CO2 standards for new cars and vans in 2020. EU legislative procedures require that any regulatory proposal by the European Commission be discussed and voted on in the European Parliament, as well as in the Council of the European Union.
In the European Parliament, the Environment Committee has the lead on regulation of CO2 from vehicles. The Committee voted on the 2020 CO2 standards in April 2013. After negotiations between the Parliament and the Council, a compromise deal was reached at the end of June 2013. However, in an unprecedented move the German Government prevented a formal vote scheduled for June 27, 2013. Another round of negotiations between the European Parliament and the Council followed. On October 4, an agreement was reached on the regulation for vans, followed by an agreement on passenger cars on November 29.
For the final agreement on cars, a phase-in provision that effectively delays the 95 g/km target from 2020 to 2021, was introduced. Both regulations must still be formally adopted by the European Parliament and the European Council. This is regarded as a formality, with no further modifications or delays expected.
Key elements of the regulations
For the regulation on passenger cars:
* A target value of 95 g/km of CO2 for 2020 for the new car fleet is set. However, there is a one-year phase-in period, requiring 95 per cent of new car sales to comply with the target in 2020 and 100 per cent from the end of 2020 onwards. Effectively, the 95 g/km target therefore applies from 2021 on.
* Vehicle weight is retained as the underlying utility parameter, i.e., the heavier a manufacturer’s car fleet, the higher the CO2 emission value allowed by the regulation. The factor used is 0.0333, meaning that for every 100 kg additional vehicle weight, the emission of 3.33 g/km more of CO2 is allowed. For the post-2020 time period, other parameters such as vehicle footprint will be considered.
* Super-credits for low-emission vehicles. Between 2020 and 2022, every car with CO2 emissions of less than 50 g/km will count more towards meeting the fleet average than cars with emissions above that cutoff. The weighting factors are: 2.00 (2020), 1.67 (2021) and 1.33 (2022). 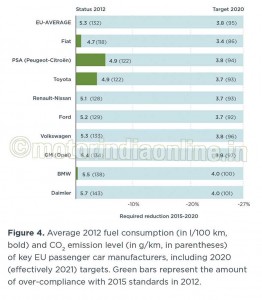 The limit for the use of super-credits, expressed as the difference between the average fleet CO2 emissions calculated with and without the application of super-credits is set at a maximum of 7.5 g/km for the three years 2020-2022 combined.
The limit for the use of super-credits, expressed as the difference between the average fleet CO2 emissions calculated with and without the application of super-credits is set at a maximum of 7.5 g/km for the three years 2020-2022 combined.
* The new test procedure (WLTP) should be applied “at the earliest opportunity”. In this context, the 2020 CO2 targets will be adjusted to the WLTP, making use of the results of a NEDC-WLTP correlation study, to ensure comparable stringency for manufacturers and classes of vehicles. Deviations between the approval CO2 emission values and “real-world” emissions should be addressed, including consideration of an independent in-service conformity test procedure that would test a representative sample of vehicles offered for sale.
* Now about eco-innovations: As was the case with the 2015 regulation, manufacturers can apply for a maximum of 7 g/km of credits for the use of “innovative technologies” whose benefits are not adequately captured by the test cycle. This applies only until the WLTP is introduced.
* Excess emission premium for manufacturers failing to meet their emissions target: EUR 95 for every g/km of excess emissions per vehicle. A previous concession, setting a lower excess emission premium for the first three g/km of excess emissions, is discontinued.
* A review clause to establish CO2 emission targets for the period beyond 2020. By 31 December 2015, the European Commission is required to review the specific emission targets, modalities and other aspects of the regulation needed to set standards beyond 2020. The review clause also states that a “clear emissions reduction trajectory, comparable to that achieved in the period to 2020” shall be maintained. The European Parliament, in its April vote, recommended an indicative target range of 68-78 g/km for 2025.
For the vans regulation:
* A target value of 147 g/km of CO2 for 2020 is set.
* Vehicle weight is retained as the underlying parameter, with a slope factor of 0.0960, meaning that for every 100 kg additional vehicle weight the emission of 9.60 g/km more of CO2 is allowed.
* The new test procedure (WLTP) should be applied “at the earliest opportunity”. In this context, the 2020 CO2 targets will be adjusted to the WLTP, making use of the results of a NEDC-WLTP correlation study, to ensure comparable stringency for manufacturers and classes of vehicles. Deviations between the approval CO2 emission values and emissions derived from vehicles offered for sales should be addressed, including consideration of an independent in-service conformity test procedure that would test a representative sample of vehicles offered for sale.
* As for eco-innovations, manufacturers can apply for a maximum of 7 g/km of credits for the use of “innovative technologies” whose benefits are not adequately captured by the test cycle.
* Excess emission premium for manufacturers failing to meet their emissions target: EUR 95 for any g/km of excess emissions per vehicle. A previous concession, setting a lower excess emission premium for the first three g/km of excess emissions, is discontinued.
* A review clause that, by December 31, 2015, requires the European Commission to review the specific emission targets, modalities and other aspects of the regulation in order to establish the CO2 emission targets for the period beyond 2020.
The situation today
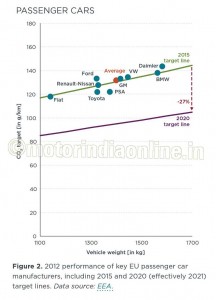
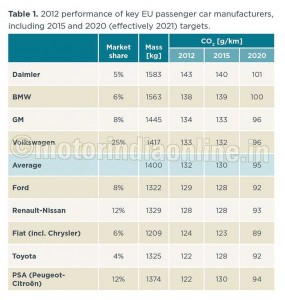
The existing CO2 regulation for 2015 passenger cars has already led to noticeable results: the average CO2 emission level of new cars dropped from about 160 g/km in 2006 to 132 g/km in 2012 as measured over the European driving cycle, a 17 per cent reduction. The annual reduction rate is about twice what it was before introduction of mandatory emission targets. Hence, the 2015 target of 130 g/km is close to being reached. Most manufacturers have met their individual 2015 target already (Figure 2).
The required reduction between 2015 and 2020 (effectively 2021, taking into account the phase-in provision) is 27 per cent for all manufacturers. The 95 g/km target for 2020 corresponds to about 3.8 liters per 100 kilometer (l/100km) of fuel consumption.
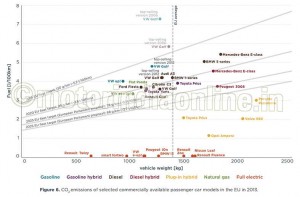
PSA and Toyota are already significantly over-complying with their 2015 targets, and are already on their way to meet their 2020 targets (Table 1 and Figure 4). There are a number of individual vehicle models that are commercially available today which already meet 2020 CO2 emission targets (Figure 6).
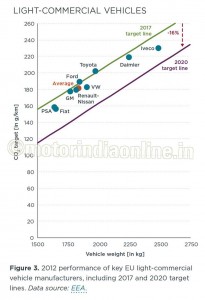
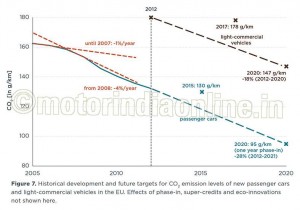
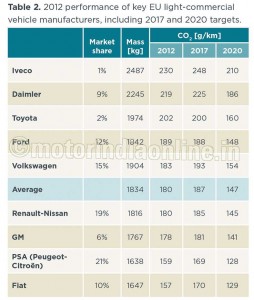
For light-commercial vehicles, the average CO2 emission in 2012 was 180 g/km. The 2017 target of 178 g/km is therefore close to being reached several years in advance (Figure 3). However, the light commercial vehicle regulation assumes an average vehicle weight of 1,706 kg for the years until 2017, while the real average weight is currently 1,834 kg. Carrying out the 2017 target calculations on this basis – as required by the regulation – the actual target for 2017 would be 187 g/km. This means that all manufacturers are already meeting their individual 2017 target in 2012 (Table 2).
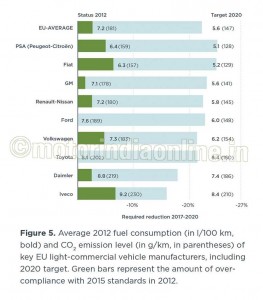
For 2020, the light commercial vehicle target is 147 g/km, which corresponds to roughly 5.6 l/100 km. For 2020, the vehicle weight used for the calculation of the fleet targets will be adjusted to reflect the real weight of the fleet. The average target will therefore be 147 g/km, independent of any future changes in vehicle weight. The required reduction between 2017 and 2020 is 16 per cent. Most key manufacturers are already overcomplying with their 2017 target, and are on the right path to meet their 2020 targets (Figure 5, Table 2).
Expected effects of the regulations
The new regulations will reduce the average CO2 emission level of new passenger cars to 95 g/km by 2020 (effectively 2021), which corresponds to a fuel consumption of about 3.8 l/100 km. For vans, it will be 147 g/km by 2020, which corresponds to about 5.6 l/100 km (Figure 7).
The annual reduction rate required between 2012 and 2020 is about 4.0 per cent for cars (3.6 per cent if taking into account the 2021 phase-in provision) and the annual reduction rate between 2012 and 2020 for vans is about 2.5 per cent. Before 2008, annual CO2 reduction rates for cars were in the range of one per cent, but increased to about four per cent with the introduction of a mandatory Europe-wide CO2 regulation and CO2 based vehicle taxation in a number of EU member-States. For light commercial vehicles, historical trend data are available to a very limited extent only.
All values given correspond to the current EU type-approval driving cycle, the NEDC. There exists statistical evidence that the “real-world” CO2 emission levels of vehicles are significantly higher, in the vicinity of 25 per cent for passenger cars. With the introduction of the new driving cycle, the WLTP, it is expected that this gap between laboratory (type-approval) and on-road CO2 and fuel consumption figures will be reduced to some extent.
In an underlying impact assessment for the original regulatory proposal (not taking into account any changes during the political negotiations with the European Parliament and Council), the European Commission quantified the expected effects of the proposed cars and vans regulations:
* Fuel cost savings per car of around EUR 340 in the first year, and an estimated total of EUR 2,904-EUR 3,836 over the vehicle’s lifetime, as compared with the 2015 target. For vans, fuel cost savings are estimated to be around EUR 400 in the first year and EUR 3,363-EUR 4,565 over the vehicle’s lifetime.
* EUR 30 billion per year in total fuel cost savings for consumers.
* An increase in EU GDP by EUR 12 billion annually and in spending on employment by EUR 9 billion per year.
* A 25 per cent reduction in fuel consumption, saving 160 million tons of oil between 2020 and 2030 at around EUR 70 billion at today’s prices.
* Avoided CO2 emissions of around 420 million tons in the period to 2030.
* Negative abatement costs for CO2 – that is, the fuel savings are larger than the cost of complying, resulting in net savings of between EUR 80 and EUR 295 per ton of CO2 avoided.
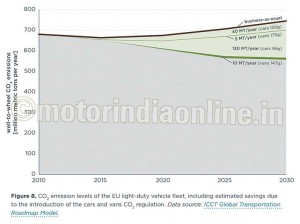
Calculations by the ICCT show that for the vehicle stock, CO2 emission levels are expected to be about 185 megatons (MT) per year lower in 2030 than in the business-as-usual scenario (Figure 8). Of these 185 MT, about 130 MT are due to the introduction of the 95 g/km cars regulation for 2020, and about 10 MT are due to the 147 g/km vans regulation. The remaining 45 MT come from the 2015 / 2017 cars and vans regulation.
International context
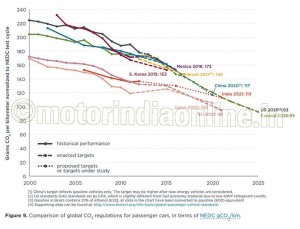
Figure 9 provides a comparison of the EU CO2 passenger car standards with similar regulations around the world. The chart converts all regulatory programs to the European test cycle to make them comparable. The EU passenger car standard of 95 g/km for 2020 (effectively 2021) can be compared to similar targets for the US (93 g/km for 2025 passenger cars), Japan (105 g/km by 2020), and China (117 g/km by 2020). The chart does not take into account any credits (such as super-credits or eco-innovations) or differences in (real-world) enforcement.
As vans make up about 10 percent of the light-duty vehicle market in Europe, the average CO2 emission standard for the EU light-duty vehicle fleet in total in 2020 will be equivalent to about 100 g/km. When taking into account light trucks, the US standard is equivalent to 107 g/km in 2025 when adjusted for the European driving cycle.
Both regulations must be formally adopted by the European Parliament and the European Council. This final step is regarded as a formality, and no further modifications or delays are anticipated.
Source: ICCT