Infineon is a global leader in advanced power and automotive electronics, the only player worldwide that combines both areas of expertise with more than 15 years of experience in electro-mobility. In this article, Ankur Oberoi, Business Development Manager (Automotive), Infineon Technologies India, elaborates about the latest products and technologies developed by the company

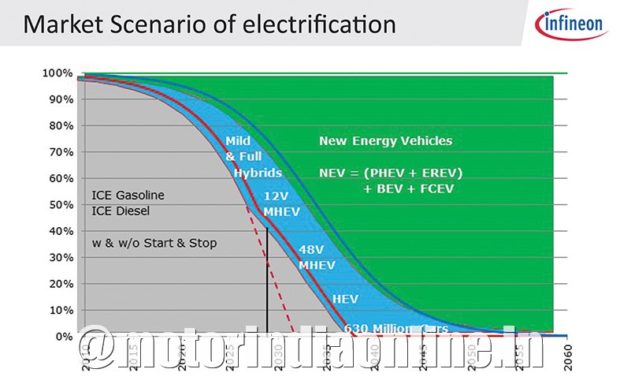
The combustion engine will continue to dominate India’s four-wheeler automobile landscape. Electrification will emerge as a strong force given the health concerns about air pollution as well as the need to be less dependent on oil import. The long-term impact of burning fossil fuel on the environment gives a strong impetus for the growth and development of fuel-efficient vehicles. India’s transition to the new age of mobility will be a gradual one. A hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) will be the bridge between internal combustion engine (ICE) and electric vehicle (EV). HEVs will play a more important role to help India achieve a balance between economic and environmental progress, along with ICE vehicles during this transition period.
HEVs are fuel-efficient with lower emissions that satisfy environmental legislations as they combine the drive powers of an internal combustion engine and an electrical motor.
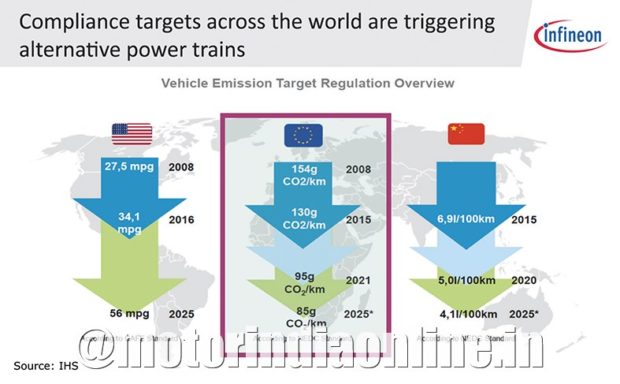
Electrification of the drivetrain requires high-power semiconductors conforming to automotive standards. Power semiconductors are the key in high-power electric drives and help to design lower cost systems. Compliance targets across the world are triggering alternative power trains.

Role of Semiconductors
Semiconductors play a key role in building more intelligence into the energy cycle. Infineon is already delivering semiconductor innovations required to resolve the challenges and design intelligent power networks, accelerating a paradigm shift toward electro-mobility on the road. Our broad and scalable product portfolio enables a smooth transition across all power classes from mild HEV to high-power EV. Infineon offers a complete portfolio of products consisting of discrete components and high-power modules ensuring fast time-to-market for our customers.
We have been a leading supplier of high-power IGBT modules for drive and traction applications for many decades. Infineon has the broadest HEV range of power modules and chips dedicated to optimising overall system cost, minimising power losses, increasing power density, maximising power savings, extending mileage and improving battery efficiency. Globally, car makers rely on products from Infineon Technologies to drive new innovations.
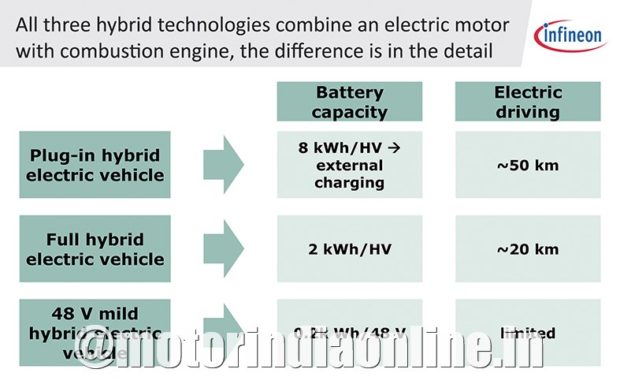
Hybrid Electric Vehicles
Though HEVs are considerably more energy-efficient than their combustion counterparts, there’s always room for improvement. Minimising power losses, maximising power savings and boosting overall performance are the constant challenges that need to be resolved as HEVs get more popular. Functional safety, including ISO 26262 compliancy, also plays an increasingly important role.
48 V Architecture
MHEV 48 V is becoming the biggest powertrain segment. With CO2 and efficiency targets getting tighter around the world, most OEMs will start implementing 2nd 48 V board net. Installing a 48 V mild hybrid system is cheaper than the cost of the penalties an OEM needs to pay to meet stricter emission standards. Basic components relevant for a Gen 1 hybrid power supply system are starter generator (smooth starting and boosting function); 48 V battery (Li-Ion or super-cap) including BMS and main switch and bidirectional DC or DC converter. For Gen 2 48 V system architecture, these would be increased boosting performance and recuperation power; beltless starter generator, electric air charger or compressor; sailing and predictive driving (ICE off at city traffic, parking, coasting), etc.
To enable coasting and sailing with ICE turned off, further auxiliaries need to be electrified like main water pump, auxiliary water pump and transmission oil pump. Cars equipped with 12 V batteries can only provide a limited amount of CO2 savings thanks to start-stop. By adding a 48 V backbone, the CO2 savings could be increased up to 20% in total. The battery, BMS and the DC-DC forms the circuitry of the 48 V system along with the starter generator as its core.
The main advantages of 48 V starter generators compared to 12 V SGs include:
- Comfort – smooth start of combustion engine.
- Enabling sailing or coasting mode – engine off during driving.
- Higher recuperation rate of up to 30 kW recuperative braking.
- Boosting of combustion engine during low RPM.
Infineon has the right system understanding to support customers in achieving their 48 V goals along with the right solutions to address this market, and hence are investing heavily in this domain.
Applications
- Main Inverter: In vehicles with an electric drivetrain, the inverter controls the electric motor. The inverter is controlled by an integrated PCB, which needs to be designed to minimise switching losses and maximise thermal efficiency. The inverter also captures the energy released via regenerative braking and feeds it back to the battery. As a result, the range of the vehicle is directly related to the efficiency of the main inverter. Our Hybrid Pack™ family enables a smooth transition across all power classes from HEV to EV from 10 kW to 180 kW. These integrated power modules contain all power semiconductors required to drive electric motors of up to 180 kW.
The Infineon® EiceDriver™ family includes single and dual-channel automotive IGBT driver ICs that provide galvanic isolation and bidirectional signal transmission. These products are ideal for the main inverter systems in automotive applications where efficiency, space savings and monitoring functions are priorities. Our highly scalable 32-bit Aurix™ family of microcontrollers provides superior performance, ASIL-D supportive functions and integrated resolver-to-digital interface. It is the perfect partner for energy-efficient electric drivetrains. Our position sensors enable close-loop feedback of the motor position for field-oriented control (FOC) that supports the highest safety levels.
- Auxiliary HV or LV DC-DC Converter: In an EV different voltage levels are required by the various electronic components. In EVs and HEVs, the DC-DC converter supplies the 12 V power system from the high-voltage battery. Designers need to increase the conversion efficiency for extending the range of the vehicle. Our chip solutions enable designers to build small DC-DC converters with a high-power density.
- Battery Management System (BMS): BMS is in charge of monitoring each of the cells included in a battery pack and ensuring that they are operated within the safe operating range. It monitors and reacts to the state of health (SoH), state of charge (SoC) and depth of discharge (DoD) with the assistance of balancing ASICs. It also prevents illegal manipulation of both the system and battery packs via integrated security on the Aurix™ microcontroller.
- Auxiliary Loads: HEVs auxiliary systems are PTC heaters and auxiliary drives. These are supplied by the high-voltage battery. These auxiliary drives can deliver power on demand and thus increase the vehicle’s energy efficiency.
- On-Board Charger: In vehicles fitted with an on-board charger unit, the battery can be charged from a standard power outlet. Charging is via the main grid calls for design flexibility due to the different voltage and current levels in different countries. The charging time is also an important factor for car drivers. System designers face the challenge of supporting the varied voltage and current levels while increasing the power density. When it comes to on-board charging, the key success factors involve efficiency and a high-power density for a small form factor.
The long-term trend is moving toward being bidirectional, where the charger also feeds power from the car to the smart grid. Our comprehensive product portfolio provides the perfect fit for compact charger units of greater than 10 kW per dm³ designed for high-switching frequencies, lower weight and adjustable displacement power factors. Our isolated gate drivers ensure safe operation.
New Generation Silicon Carbide
The use of Silicon Carbide (SiC)-based components has the potential to make vehicles affordable and lightweight due to their advantages of minimising power losses, increasing power density, maximising power savings, extending mileage and improving battery efficiency. The demand for plug-in hybrid and all-electric vehicles (xEV) continues to rise. These vehicles currently use power electronics based on silicon. However, the latest xEV designs call for advances in efficiency and power density.
SiC is emerging as the material of choice for overcoming the performance plateau of silicon. Highlights such as low switching losses, a high-temperature capability and high-switching frequency make it ideal for meeting the highest xEV requirements. SiC-based solutions promise to be more efficient, compact and lighter than conventional applications. Use of SiC means reduction of size by factor of 3-5 due to high power density. Due to increased power density the system size reduces and scalable systems can be developed while low inverter loss means savings for HV battery. Infineon has developed one of the broadest technology portfolios available on the market. We have the expertise in silicon, SiC and gallium nitride (GaN), complemented by innovative packaging and gate driver solutions.